Disc brakes are distinguished according to the driving mode, which can be divided into: hydraulic drive, wire pull drive, and wire pull hydraulic drive.
1. Hydraulic drive
The principle is to use oil as the medium, compress the oil through the piston in the brake lever, and transfer the pressure to the caliper through the oil to rub the disc to play the role of braking. This is what people often call the "oil disc"; generally speaking, the oil pipes of hydraulic disc brakes are not affected by bending. Even if the oil pipes are folded to a more complicated angle, they can still provide excellent braking force. Most of the road models of the line choose hydraulic disc brakes. On the other hand, because hydraulic disc brakes must first ensure the sealing properties during transmission using oily objects, hydraulic disc brakes lose less force during transmission, and the force is direct, so gently pinch it down It can provide powerful braking force, which is one of the biggest advantages of hydraulic disc brakes. At the same time, due to its closed system, the inside of the tubing is not invaded by dust and the maintenance period is long.
Compared with the advantages of hydraulic disc brakes, the comprehensive promotion of hydraulic disc brakes shows that its shortcomings can almost be ignored in daily use. The most important disadvantage is that on the one hand, the weight advantage is not large, and on the other hand, it is more troublesome to install and replace. Especially the application of the inner wiring frame requires disassembly and oil filling, which greatly increases the working time.
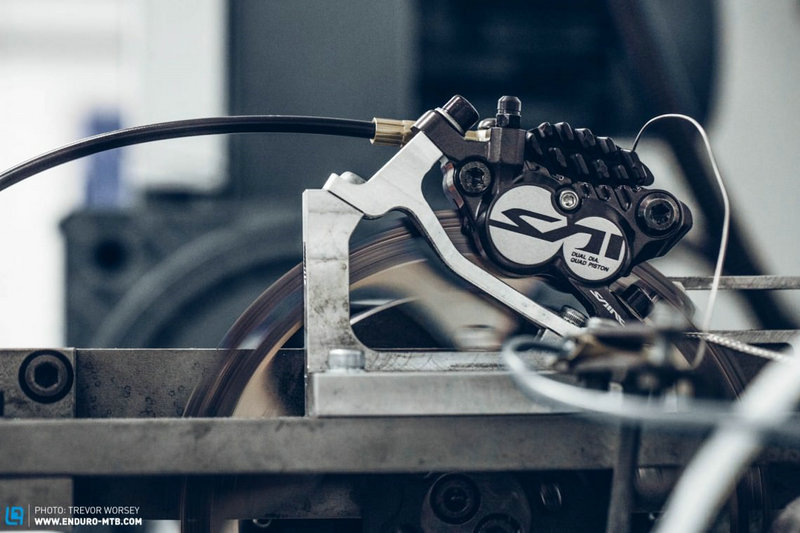

This is what people often call the "cable disc". The brake pads in the caliper move to rub the discs by the pull of the brake wire to produce a braking effect. Cable discs have greater advantages in weight and maintainability, and are usually cheaper than oil discs of the same grade. This is one of the reasons why low-end disc brakes will choose cable discs. On the other hand, when using the cable disc to upgrade from the clamper model, there is no need to change the hand change. However, because of the need for brake cables, the wiring of the cable tube cannot be bent significantly. When the fully hidden wiring method is now an advanced choice, the cable disc is almost invisible in the selection of high-end models; At the same time, the braking force of the cable disc is less than that of the oil disc, which makes many riders less confident when going downhill, and makes the film more difficult to adjust than the oil disc, and the probability of rubbing the disc is greatly increased.

3. Wire pull hydraulic drive
The development of this product was made in the early stage to compensate for the delay in the development of the transmission kit manufacturer for the hydraulic manual change. It is also aimed at many who want to upgrade the disc brake but do not want to replace the manual change, or want to neutralize the cumbersome installation of hydraulic disc brakes. It is a balanced product made with heavier weight.
Its basic principle can be divided into a wire pull cylinder, which is directly pulled through the cylinder to connect the caliper or the brake wire. The former was used on the Giant model and has now been eliminated. The latter is currently the mainstream way of line-to-oil disc brakes. This design is close to hydraulic drive in terms of braking force, and is relatively low in weight and price, and easier to maintain. The disadvantage is that it still can't adapt to the full internal wiring design, and wiring needs to be considered.

Flat mount clamp

Compared with the paperback specification, the size is smaller, lighter, and more beautiful. It is undoubtedly a good solution when road bikes are very sensitive to weight. The interface of the flat mount clamp is more compact, which is conducive to the integration with the front fork. The biggest difference is that the screw is directly screwed into the clamp from below and fixed from the frame. In addition to the screw tightening method, the clamp has other structures such as oil pipes and pistons. The structure and so on are the same as direct mounting.
Direct mount clamp

The early clamps adopted the design of mountain bikes. Two fixing screws passed through the clamps from above and fixed to the frame or front fork. Due to the difference in the size of the discs, large adapters were often needed. Increased weight and reduced aesthetics. Due to the smaller selection of disc diameters on road vehicles, the importance of this wide-range adjustable design has been reduced and gradually replaced by flat mount clamp.
 +86-592-578 6546
+86-592-578 6546 info@carbonalbike.com
info@carbonalbike.com English
English français
français Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский italiano
italiano español
español português
português 日本語
日本語 한국의
한국의 Polski
Polski